Akka Streams Intro
1) The First experience
This file is a quick explanation of basic Akka Stream elements : Source, Flow and Sink. Akka Stream has very good documentation where everything is explained so there is no need to repeat it here : http://doc.akka.io/docs/akka/2.4/scala/stream/stream-quickstart.html
We are going to see in practice how to connect elements mentioned above to create a complete stream :
val source: Source[Int, NotUsed] =Source(1 to 15 by 3)
val flow: Flow[Int, String, NotUsed] =Flow[Int].map(_*2).map(i=>s"as string : $i")
val sink: Sink[Any, Future[Done]] =Sink.foreach(println)
val stream: RunnableGraph[NotUsed] =source.via(flow).to(sink)

The NotUsed type tell us that our stream doesn't materialize any additional values. We are going to take a look at materialization later - for now let's see a quick example how to materialize result future when running a stream.
val streamWithResult: RunnableGraph[Future[Done]] =source.via(flow).toMat(sink)(Keep.right)
Where are actors?
Till now we saw only constructs from Streams API - now let's see how we can integrate this API with actors. We are going to direct stream flow into an actor which is configured as a sink
class ActorSink extends Actor{
override def receive: Receive = {
case msg => println(s"Real actor received $msg")
}
}
val actorSink=system.actorOf(Props[ActorSink])
val realActorSubscriber: Sink[Any, NotUsed] = Sink.actorRef(actorSink,"MY_COMPLETED")
source.via(flow).to(realActorSubscriber).run()
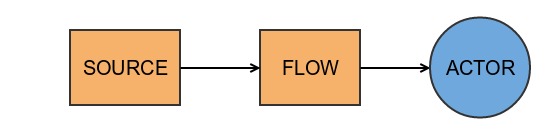
Materializers
Materializers allow stream to return auxiliary objects which can influence the way on how information is moving through stream :
For Example :
val source: Source[Int, ActorRef] =Source.actorRef
This way we have created a Source of Int elements with auxiliary Actor Reference. Now we can use this reference to provide information into the Stream.
The same situation can be seen in case of sink. Because Sink is on the righ side of a stream and by default ("via" method) left materializer is returned, then you need to explicitly state which one auxiliary value do you want to materialize.
val p5: Sink[Int, Future[Int]] = flow.toMat(sink)(Keep.right)
You can also materialize objects from both ends of a stream
val p8: RunnableGraph[(ActorRef, Future[Int])] =source.via(flow).toMat(sink)(Keep.both)
Exercise
Exercise : Basic Stream
As an input you have :
val numberCandidates: List[String] = List("1", "2", "c", "4", "e", "6", "g", "h", "9")
Filter out letters , keep only numbers, convert to int and add.
Exercise : Reading from database

You have a database with products :
private val data = Map(
1 -> Product(1, "Techno Greatest Hits 1995-97", BigDecimal(20)),
2 -> Product(2, "Bazooka", BigDecimal(120)),
3 -> Product(3, "MAc Book USB adapter", BigDecimal(1000))
)
Create source from the future :
Source.fromFuture(Database.selectAll())
Extract prices from products and sum them inside actors.
NOTE:
We need to create an alias for immutable Iterable because akka streams expects this type and standard scala library
//in akka stream
type Iterable[A] = scala.collection.immutable.Iterable[A]
//in scala package
type Iterator[+A] = scala.collection.Iterator[A]
val Iterator = scala.collection.Iterator
Exercise : Actor with ACK
To use back pressure we can assign a special protocol to an actor where every new message is explicitly requested

Implement variant of latest exercise with ACK actor
2) Integration
Next we will see how to integrate Streams with Actors and external system at the beginning and during flow processing.
mapAsync
To send information to an actor or any external system we can use mapAsync method which operate on Future.
So :
- In case of an actor we need to use ask pattern
- In case of asynchronous API which returns Future we just need to call it
- In case of synchronous API we need to trigger call in separate thread and return Future
In the example below we are using ask pattern to receive an info from an actor.
val flow: Flow[Int, String, NotUsed] =Flow[Int]
.mapAsync(parallelism = 5)(elem => (actor ? elem).mapTo[String])

queue
To Integrate stream generations with actors we can create source connected with a queue :
//PREPARING QUEUE
val source: Source[String, SourceQueueWithComplete[String]] =
Source.queue[String](bufferSize = 4, overflowStrategy = OverflowStrategy.backpressure)
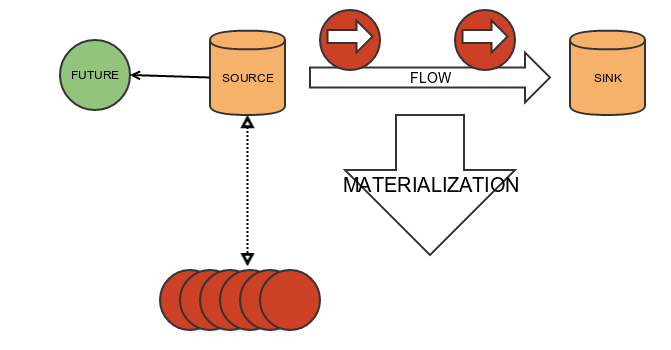
Queue is materialized when the graph is run and we each element sent to a queue flows through the stream
val queue: SourceQueueWithComplete[String] =graph.run()
//QUEUE IS GOING TO BE USED BY AN ACTOR
val actor=system.actorOf(Props(new Deduplicator(queue)))
class Deduplicator(q:SourceQueueWithComplete[String]) extends Actor{
var history=Set[String]()
override def receive: Receive = {
case s:String if(!history.contains(s)) =>
history = history + s
q.offer(s)
}
}
Exercises
Exercise : Integration with DB
Exercise : Log analysis
3)Graphs
Graphs DSL allows you to break from linear data processing. You can easily add additional data processing paths.
//GRAPH DECLARATION
import GraphDSL.Implicits._
val graphWithDomainLogging=GraphDSL.create(){implicit builder =>
val broadcast=builder.add(Broadcast[String](2))
val additionalOutput=Sink.actorRef(domainActor,"COMPLETE_MESSAGE")
broadcast.out(0) ~> additionalOutput
FlowShape(broadcast.in,broadcast.out(1))
}
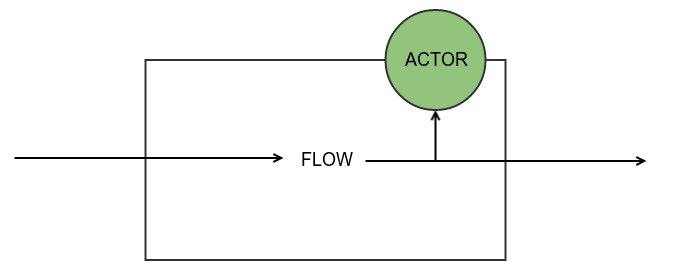
When graph is constructed you cna easily create a flow from it
val flow=Flow.fromGraph(graphWithDomainLogging)
Exercises
Exercise : source and sink from graph