Traits Linearization
During those workshops we will see how exactly we can compose multiple traits and how they this mechanism solves so called "Diamond Problem.".
Java 8 and default methods
FILE : starter.traits.JavaDefaultMethods
To have a comparison let's first check similar mechanism to traits which is available in java8. In this version of java you can have a default implementation of an interface method however when two interfaces have the same method with default implementation you are the one responsible for solving this conflict.
interface One{
default String method(){
return "one";
}
}
interface Two{
default String method(){
return "two";
}
}
class Example implements One,Two{
@Override
public String method() {
//you need to choose
return One.super.method() + " example";
// return Two.super.method() + " example";
}
}
Scala multiple traits inheritance
FILE : starter.traits2.Linearization
In Scala this is solved differently. You can easily inherit from multiple traits and call super in each one. Scala will rearrange traits from right to left.
If some traits are repeated in hierarchy than linearization removes repetitions. Algorithm is not simple and visualization can be seen on image below. Generally if you need to understand this algorithm to understand your code - maybe it's time for refactoring
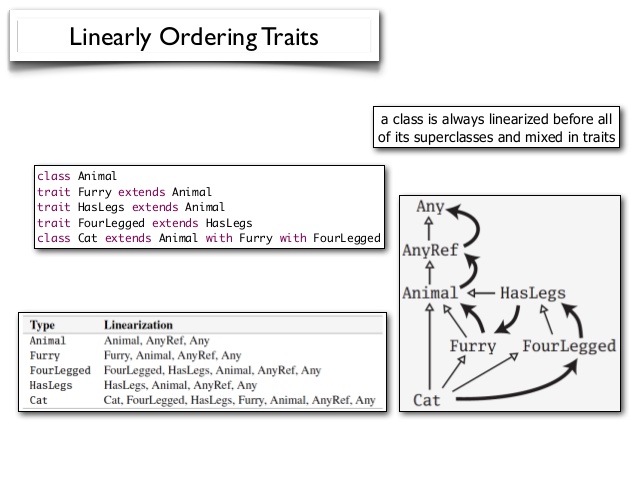
override abstract
If you want to attach given trait to particular hierarchy by extending the hierarchy root -> then you can not just call super because super is abstract. you need from one side to point that you are overriding a method and on the other force concrete class to implement it -> so you have modifier abstract override
abstract class DemoReader{
def read:Char
}
trait DiagnosticRead extends DemoReader{
override abstract def read:Char={...
Exercises
Implement web controller and security filters
FILE : traits2.exercises.LinearizationExercises TEST FILE : traits2.exercises.LinearizationExercisesTest
Part 1
Finish implementation
class ShopController extends Controller{
override def handle(r: Request): Response = ???
}
so that it can handle requests from test
val r=new Request("/shop","chrome","lodz",new Auth("login","password"))
and for the rest returns 404.
Part 2
Implement two filter which will be mixed into controller :
trait LocationFilter extends Controller{
abstract override def handle(r: Request): Response = ???
}
trait LocationMaskingFilter extends Controller{
abstract override def handle(r: Request): Response = ???
}
so that request from banned country be filtered out:
val r=new Request("/shop","chrome","BANNED_COUNTRY",new Auth("login","password"))
val response=controller.handle(r)
response.status mustBe 403